HOW IT WORKS
INFRA builds automated solutions that include scanning and hacking technologies for Assessment and Intelligence.
We prefer a Heuristic method (an estimation of the likelihood of an event made by comparing it to the most typical example of an event that already exists in our database) rather than a simple signature database to find out the vulnerabilities. Using a trial-and-error approach (Fuzzing and Bruteforce), Machine Learning will create Rules-of-Thumb based on previous experiences, which lead to Ansatz Educated-Guess of potential vulnerabilities. Whenever possible, using the integrated hacking platform, the potential vulnerabilities detected will be validated by exploiting (hacking) them automatically. This approach is very successful in attacking databases and web applications, especially when they are customized and there are no versions of CMS to match in the database. Heuristic automation is better to find more and verify more, limiting human errors and maximizing reliability. All controls in IoT, servers, databases and Web applications are standardized and automated, speeding up Vulnerability Assessment and the Penetration Testing (VAPT).

Input/Output validation

Specific problems

Configuration errors
The most common application vulnerabilities in recently tested applications include:
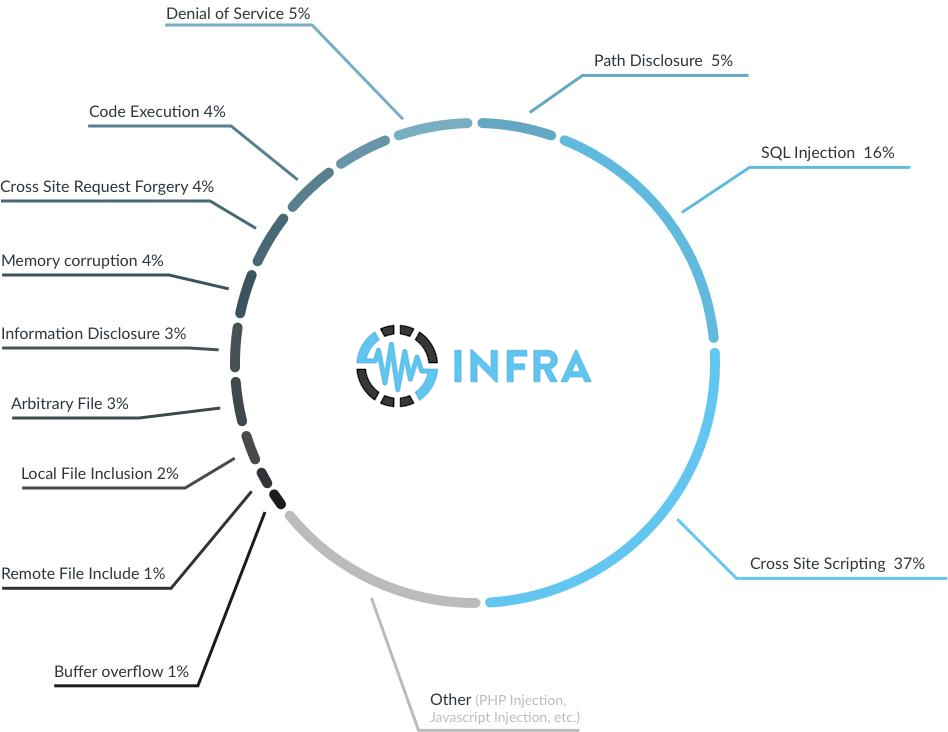
INFRA modules are programs that make possible each test and are divided into 8 groups:
1. IG – Information Gathering
Modules that allow to search the required information in other security modules and also in intelligent modules in order to run deeper target and company analysis.
2. SA – Service Assessment Modules focused on searching the required information in other security modules, identifying the doors, services and OS, software versions and creating rules to launch other modules over revealed services.
3. US – User & Session Modules created to search vulnerabilities related to users, cookies, login, multi- session, etc.
4. VA – Vulnerability Assessment Modules that search vulnerabilities related to system and network, such as configuration, buffer overflow, software obsolescence and system-related problems, services and network.
5. WA - Web Assessment Modules that search vulnerabilities related to servers, services and web applications. All OWASP top 10 vulnerabilities are tested very carefully.
6. DB – Data Base Assessment Modules that search database-related vulnerabilities.
7. IF – Intelligence Framework extra modules This group contains all modules to look for the required information for other security modules.
8. EM - External Modules INFRA can also be connected to other (optional) vulnerability scanning software, commercial and open source, to get more information that will be used in its modules
- Machine Learning: Intelligence Framework is the first company to develop a turnkey solution for mandatory assessments, other solutions requires mainly the experience of the human analysts. Without automation and machine learning, security is significantly more manpower intensive, relying on people and their knowledge to detect, investigate, report and remediate, with a large percentage of the actions taken by security teams being repetitive. The skills shortage, combined with the ever-increasing need for organizations to achieve efficiency, necessitates new technologies to accelerate time to detection, response and recovery. By strategically implementing automation and machine learning to the assessments it will save time and improve effectiveness, enterprises can eliminate wasteful processes that rely on analysts sifting through piles of data and alerts to find actual threats.
- Platform Consolidation: We have been building out security platforms through technology acquisition and new feature development. These integrated platforms provide interconnected functionality, which enables consolidated management that is far more efficient than managing disparate point tools.
- Automation and Orchestration: Security automation and orchestration accelerates the movement of data between tools for the purposes of threat prioritization, response amplification, labor reduction and consistent workflow. This sector of security has seen massive investment and adoption, due to its promise to relieve security personnel of routine manual labor, and to implement effective workflows.
- Continuous Security Validation: Once these integration, consolidation and automation strategies are in place, enterprises must have systems to test that their security controls are properly configured over the course of time, even as network changes are made. Continuous security validation automates and speeds the process of identifying misconfigured platforms and network devices.



